Table of Contents
1. Crawling – Discovering Content on the Web
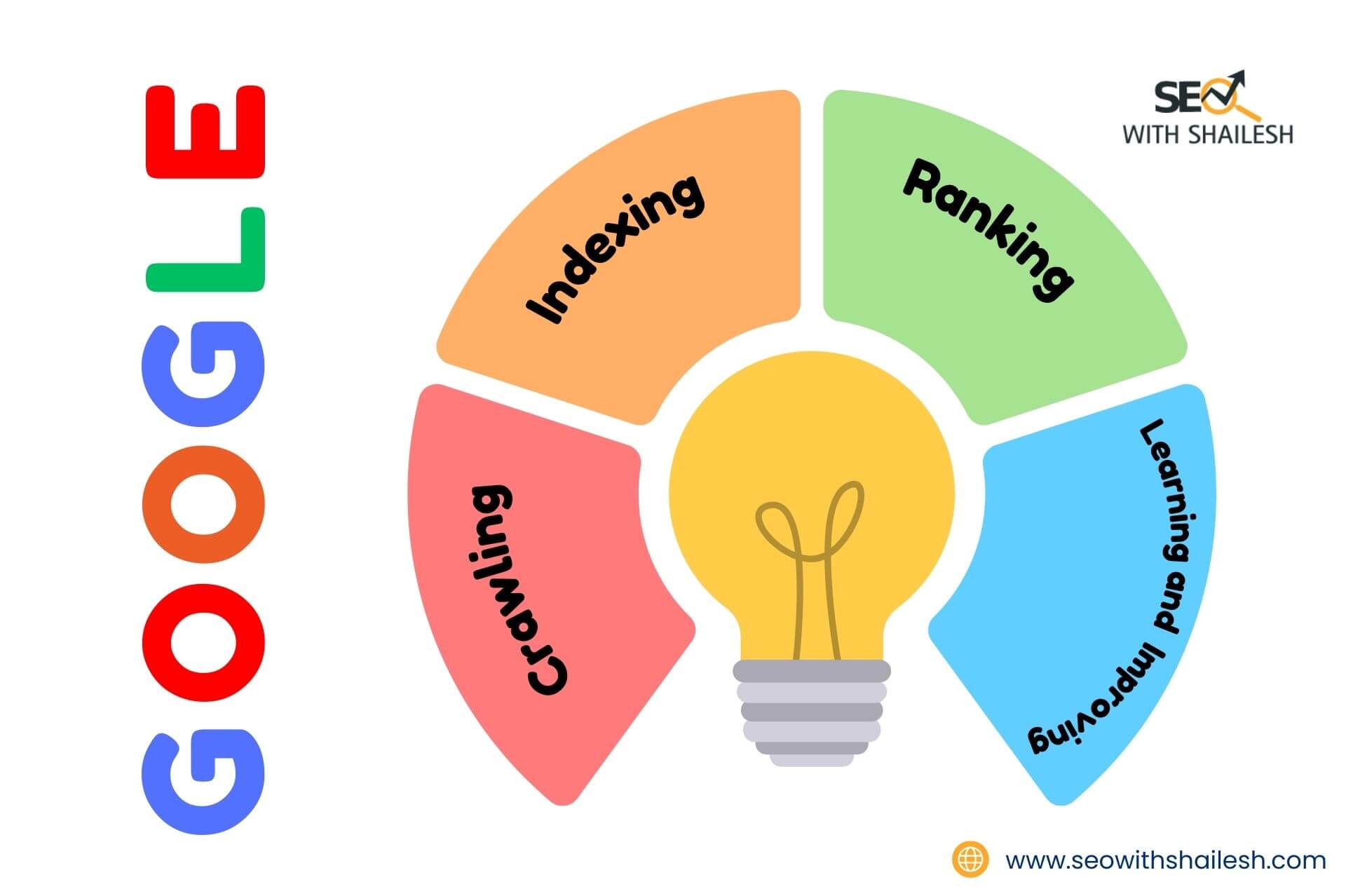
The first step in this process is called crawling. Search engines like Google use specialized programs, known as crawlers or spiders, to navigate and explore the internet. Think of these crawlers as small robots moving from one page to another, discovering all the content available.
- How it works: Crawlers find pages by following links from one page to the next. Just like you would click on a link to go to a new website, crawlers follow these links to collect data on each page they find.
- Why it’s important: Without crawling, search engines wouldn’t know your website exists, which means it wouldn’t show up in search results.
Key takeaway: Crawling is how search engines find all the pages on the web.
2. Indexing – Organizing Information
Once a crawler finds a page, the search engine stores the information in a huge database called an index. This is like a digital library that holds a copy of every page that the crawler has found.
- How it works: Search engines look at the page’s text, images, videos, and links to understand what each page is about. They might also check other information on the page, like the title, headings, and descriptions, which help give clues about its topic.
- Why it’s important: Indexing makes it possible for search engines to organize millions of pages, so they can quickly find the best results for a search.
Key takeaway: Indexing is how search engines store information to easily access it later.
3. Ranking – Deciding Which Results Come First
After indexing, search engines need to figure out which pages to show and in what order. This is called ranking. When you type a query into a search engine, it looks through its index and picks the most relevant pages to display at the top.
- How it works: Search engines use special rules, called algorithms, to rank pages. These algorithms consider many factors, such as:
- Keywords: Does the page have words that match your search?
- Page quality: Is the information accurate, up-to-date, and useful?
- Authority: Do other websites link to this page, showing it’s trusted?
- User experience: Is the page easy to read and navigate?
- Why it’s important: Ranking helps you find the most relevant and reliable information for your query without scrolling through endless pages.
Key takeaway: Ranking is how search engines sort results so the most helpful pages appear first.
4. Understanding User Intent
Search engines want to understand why you’re searching for something, not just what you’re searching for. This is called user intent. Are you looking for information? Trying to buy something? Or maybe you want directions to a place?
- How it works: Search engines use clues in your query to understand your intent. For example:
- If you type “best dental clinic near me,” the search engine knows you’re looking for dentist places nearby.
If you type “best dental clinic near me,” the search engine knows you’re looking for dentist places nearby.
If you search “how to make Palak Paneer,” it assumes you want a recipe.
Why it’s important: Understanding user intent helps search engines show the right type of content, so you don’t waste time on pages that don’t match what you need.
Key takeaway: User intent helps search engines give you the right kind of answer, depending on what you’re looking for.
5. Learning and Improving Over Time
Search engines constantly improve by learning from user behavior and updating their algorithms. These updates are why search results keep getting better and more accurate.
- How it works: Search engines analyze what people click on, how much time they spend on a page, and whether they come back to search again. This information helps them understand which pages are truly useful. Search engines also make regular changes to their algorithms to improve the quality of search results.
- Why it’s important: Constant learning and improvement mean search engines stay updated with new websites, information, and user trends, giving you better search experiences.
Key takeaway: Search engines are always updating to give you the best possible answers.
Summary
To sum it all up, here’s how search engines work:
Learning and Improving – Constantly updating to provide better answers.
Crawling – Finding content on the web by following links.
Indexing – Storing information in a digital library.
Ranking – Sorting results to show the most relevant ones first.
Understanding User Intent – Figuring out what you need based on your search.